Overview & Concepts
Self-hosted Appcircle enables you to use your own systems and infrastructure for all cloud features.
By this way, you can build and test your apps on your choice of architectures. You have full control over the build environment. You can also customize your Appcircle installation with various options.
With the help of self-hosted runners as connected agents, you can have whole Appcircle in your own infrastructure and use all Appcircle features in your private cloud without any limitations.
Self-hosted Appcircle section in here, gives you detailed information about only server-side components installation and other related operations. For details about self-hosted runner concept, see Self-hosted Runner section in docs.
The only requirement for using self-hosted Appcircle is to be in enterprise plan.
See pricing and feature comparison table for details.
Docker/Podman Standalone Architecture
We generally recommend a standalone approach by deploying a single node environment for the Appcircle server to reduce the complexity a little further.
When we look at self-hosted Appcircle deployment as a whole, we will see below architecture in execution for a basic installation.
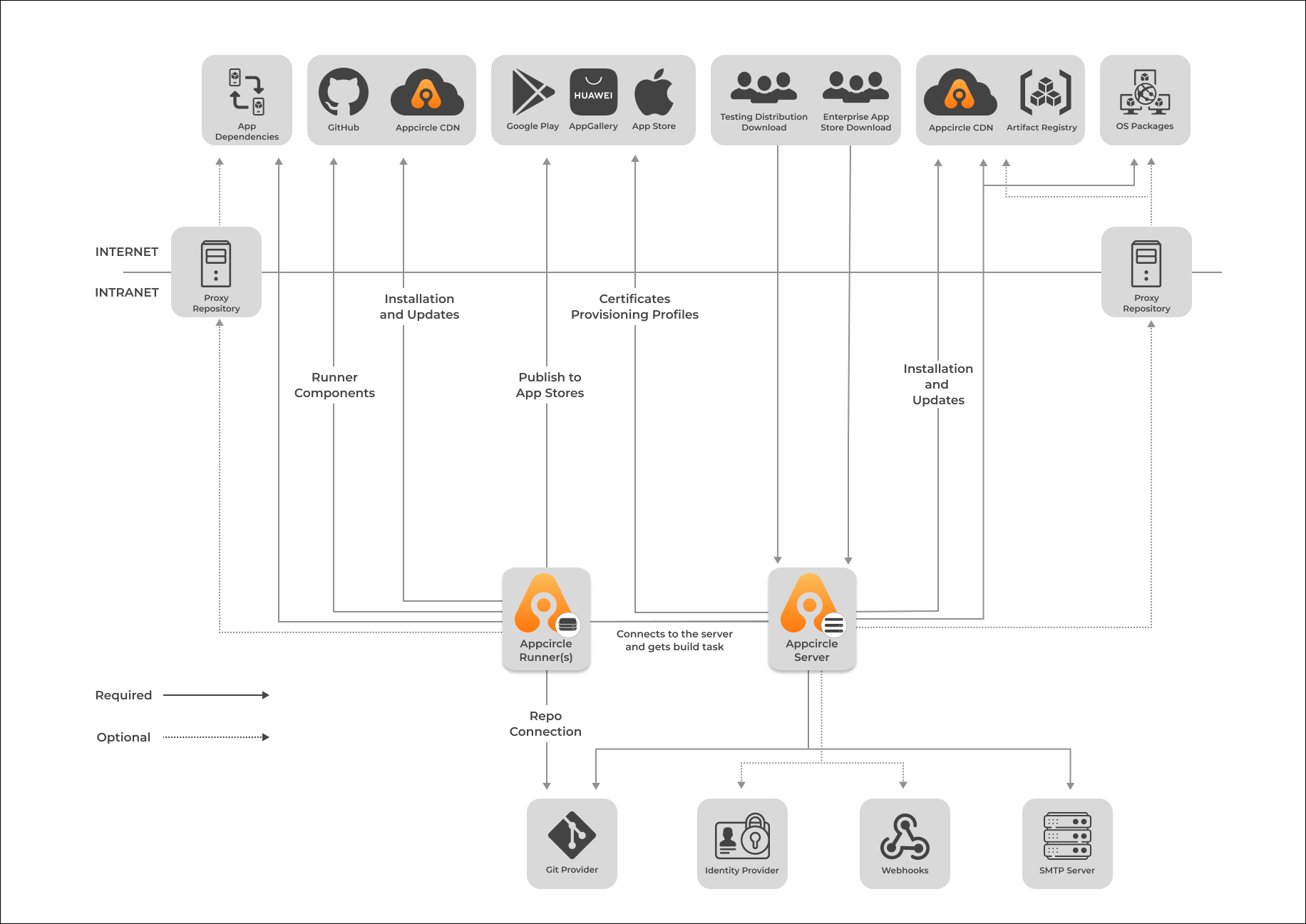
To see the topology diagram in greater detail, click here. It will open the diagram in new browser tab.
You can see all external network access details on the Network Access page.
Docker/Podman Architecture With DMZ Support
If you plan to use the Enterprise App Store and Testing Distribution modules isolated from the internal network in which these modules are only exposed to the external networks, you can use Docker/Podman Architecture in DMZ formation.

For more information about the Appcircle DMZ architecture, you can check the Enterprise App Store and Testing Distribution in DMZ document.
Kubernetes/OpenShift Architecture Using Helm Chart
In addition to the standalone and DMZ architectures, you can deploy Appcircle using the Helm chart for Kubernetes/OpenShift environments. This method allows for greater scalability and management flexibility.
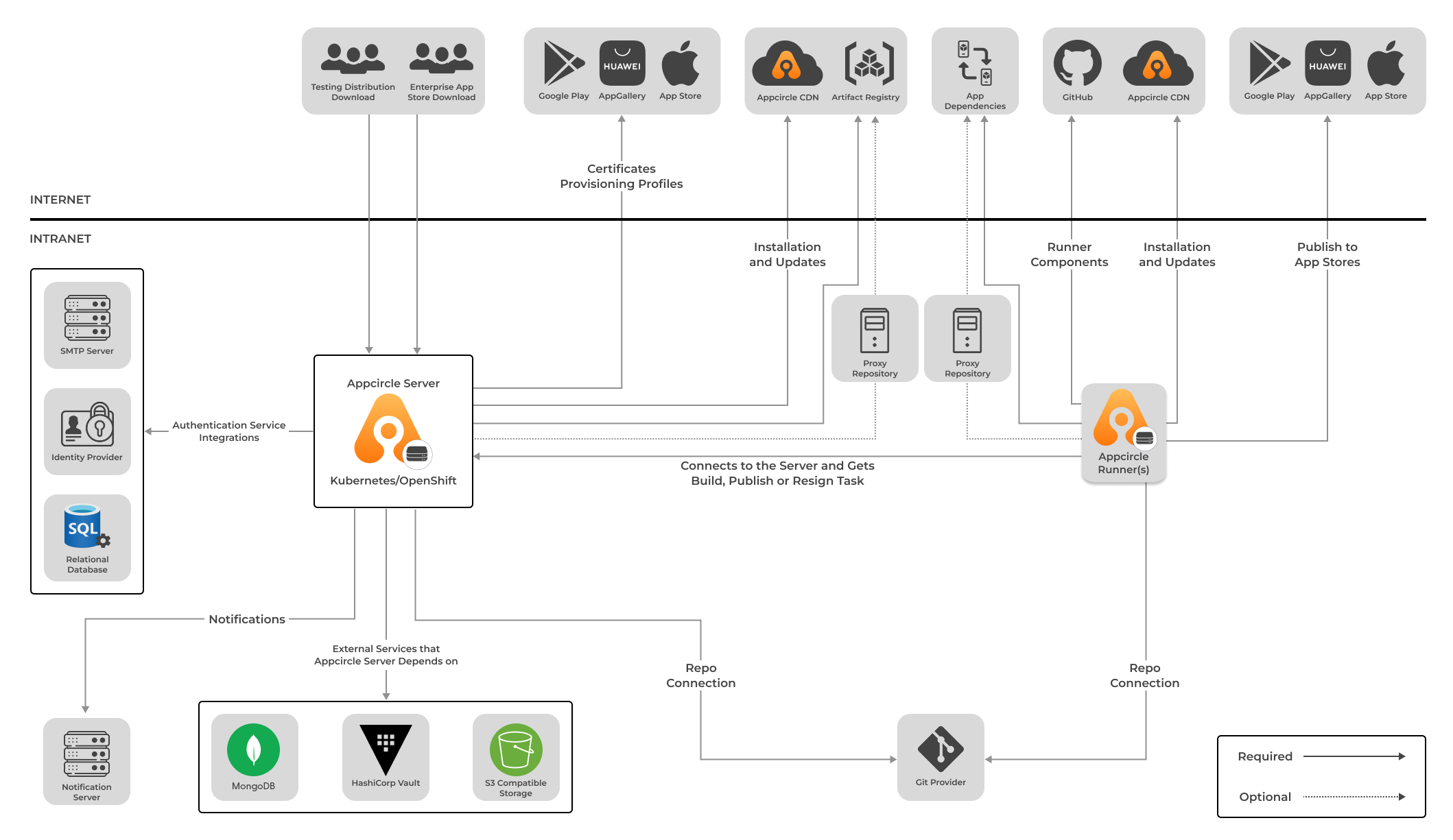
For detailed instructions on installing and configuring Appcircle using the Helm chart, refer to the relevant Helm chart installation documentation for Kubernetes or OpenShift. These documentation pages include steps for setting up Helm, configuring values.yaml, and deploying the Appcircle server.
Advantages
- High Availability: Deploying on Kubernetes/OpenShift ensures high availability through automated failover and load balancing.
- Scalability: Supports high traffic and large-scale applications with horizontal scaling based on load, ensuring optimal performance. Easily scale your deployment by adding or removing nodes in the Kubernetes/OpenShift cluster.
- Fault Tolerance: Kubernetes/OpenShift can handle node failures and automatically reschedule workloads to maintain application uptime.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Requires familiarity with Kubernetes/OpenShift and Helm, which can be complex to learn and manage.
- Resource Requirements: May require more resources compared to a single-node deployment, including more compute power and storage.
- Operational Overhead: Maintaining and monitoring a Kubernetes/OpenShift cluster can add operational overhead.