Android Sign
Android Sign step signs your APK or AAB with the given Android keystore and exports a binary file compatible with Android devices.
This step follows the Android Build step to sign the unsigned build output if the project doesn't include a keystore. If your project includes a keystore, the build application step will generate a signed artifact. If you do not disable this step, your artifact will be unsigned and then re-signed using the keystore selected in the Configuration or in this step.
As noted in the Android Developer documentation:
If the build variant you've selected is a debug build type, then the APK is signed with a debug key and it's ready to install. If you've selected a release variant, then, by default, the APK is unsigned and you must manually sign the APK.
When you build your app with the debug variant and select a keystore in configurations, the Android Sign step will replace the default debug signing files and re-sign the app using the specified keystore files.
Prerequisites
Before running the Android Sign step, you must complete certain prerequisites, as detailed in the table below:
| Prerequisite Workflow Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Git Clone | This step relies on the Android Build step and the Git Clone step is necessary for the Android Build step to run successfully. |
| Android Build | The app required for this step is generated by the Android Build (or alternative build steps). |
If a step other than the Android Build step is used to build an app, then the Android Sign step depends on this step.
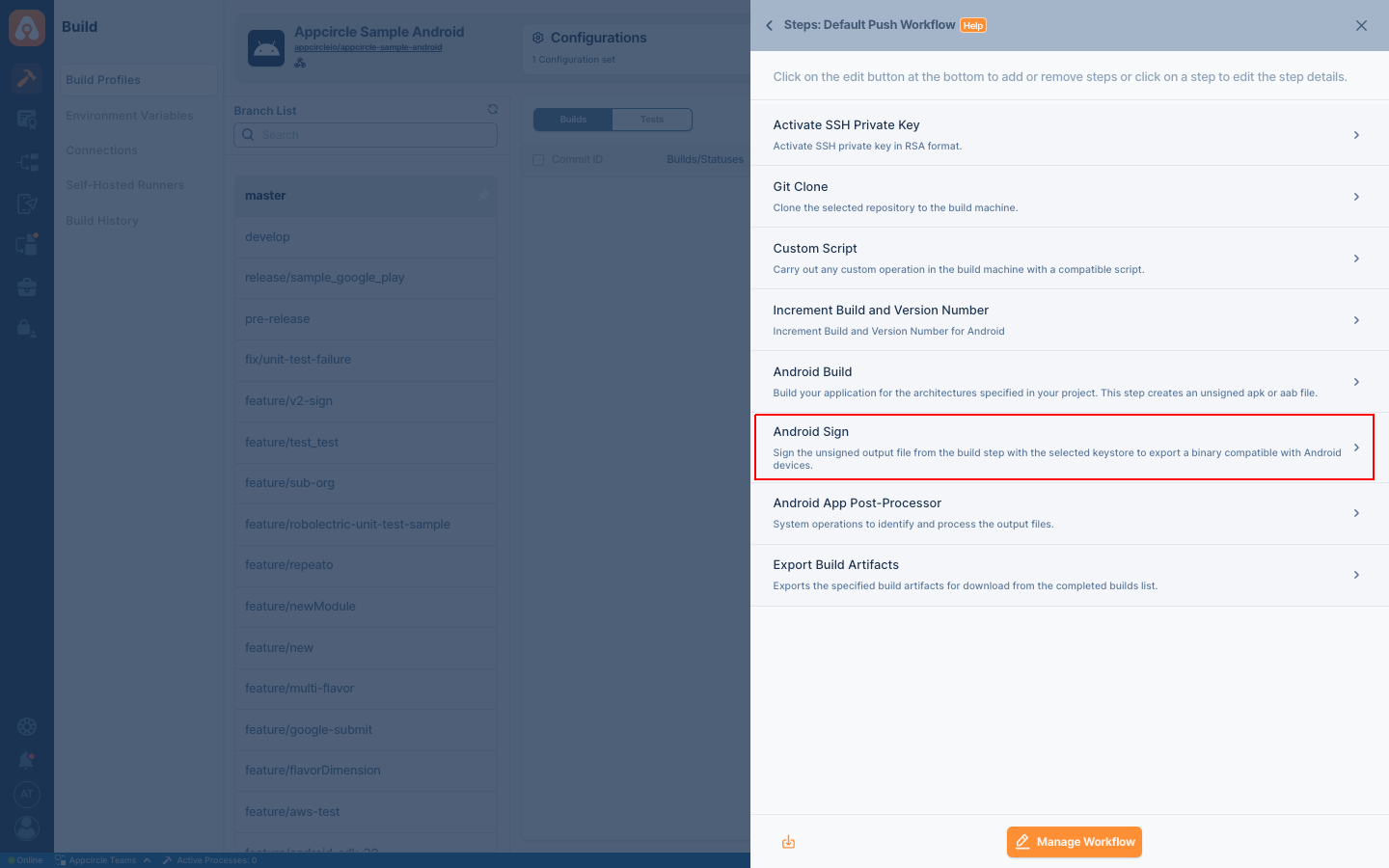
To share the signed apps created as an output of this step or to view them on the Download Artifacts page, please ensure that the Export Build Artifacts step is included in your workflow after this step.
Input Variables
This step contains some input variable(s). It needs these variable(s) to work. The table below gives explanation for this variable(s).
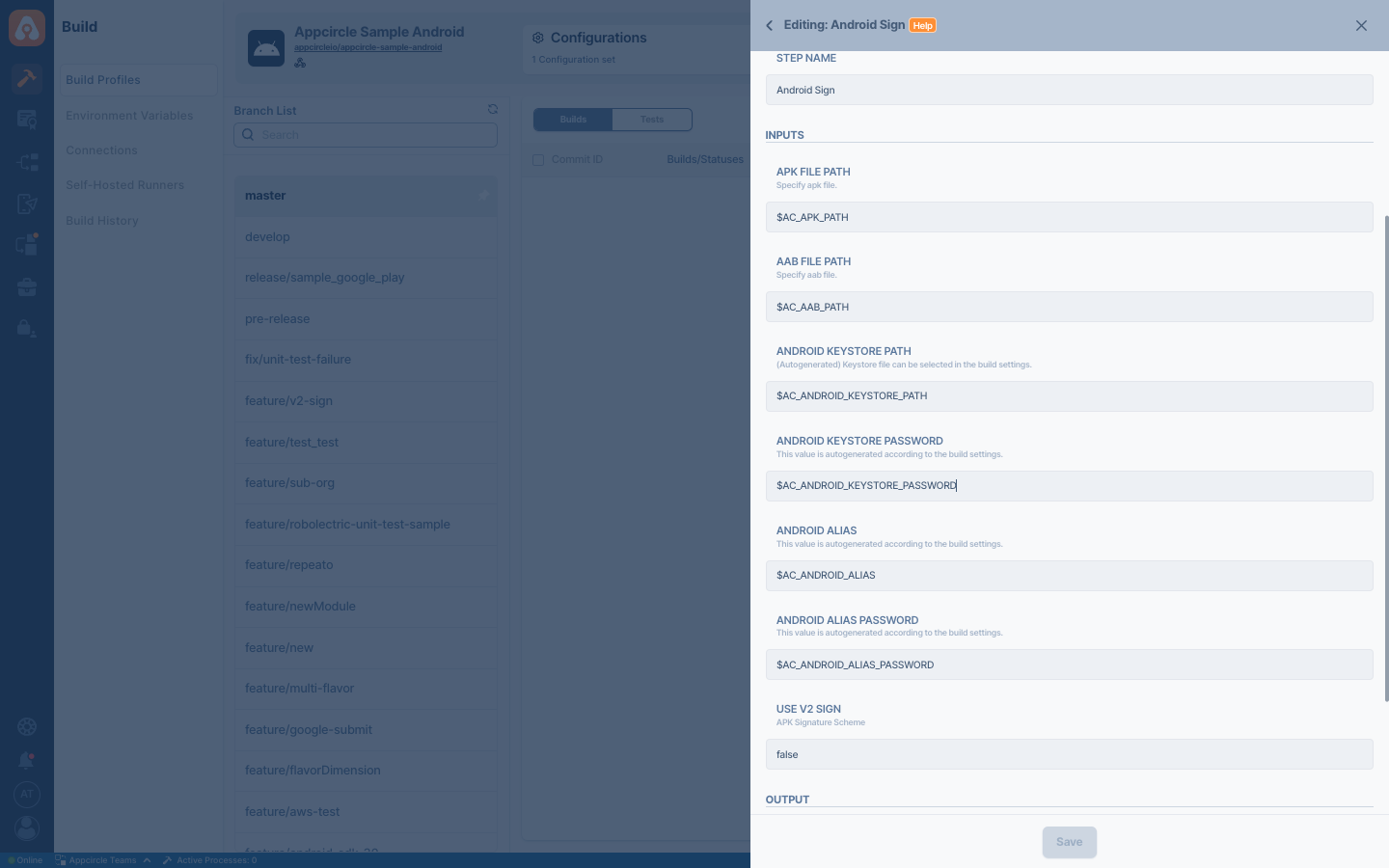
| Variable Name | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
$AC_APK_PATH | The path of the APK file. This path is automatically generated in the Android Build step. You may need to modify this input variable to provide a different path. | Required |
$AC_AAB_PATH | The path of the AAB file. This path is automatically generated in the Android Build step. You may need to modify this input variable to provide a different path. | Required |
$AC_ANDROID_KEYSTORE_PATH | Keystore file can be selected in the Configuration. This value will be auto-generated depending on your keystore file selection in signing configuration on Appcircle. | Required |
$AC_ANDROID_KEYSTORE_PASSWORD | Password for the selected keystore file. This value will be auto-generated based on your keystore file selection. | Required |
$AC_ANDROID_ALIAS | Alias name for the selected keystore file. This value will be auto-generated depending on your Configuration | |
$AC_ANDROID_ALIAS_PASSWORD | Alias password for the selected keystore file. This value will be auto-generated depending on your Configuration | |
$AC_V2_SIGN | Defaults to false. Set true if the signature should be done using apksigner instead of jarsigner. For more information, Apps targeting Android 11 require APK Signature Scheme v2. | Optional |
Output Variables
The output(s) resulting from the operation of this component are as follows:
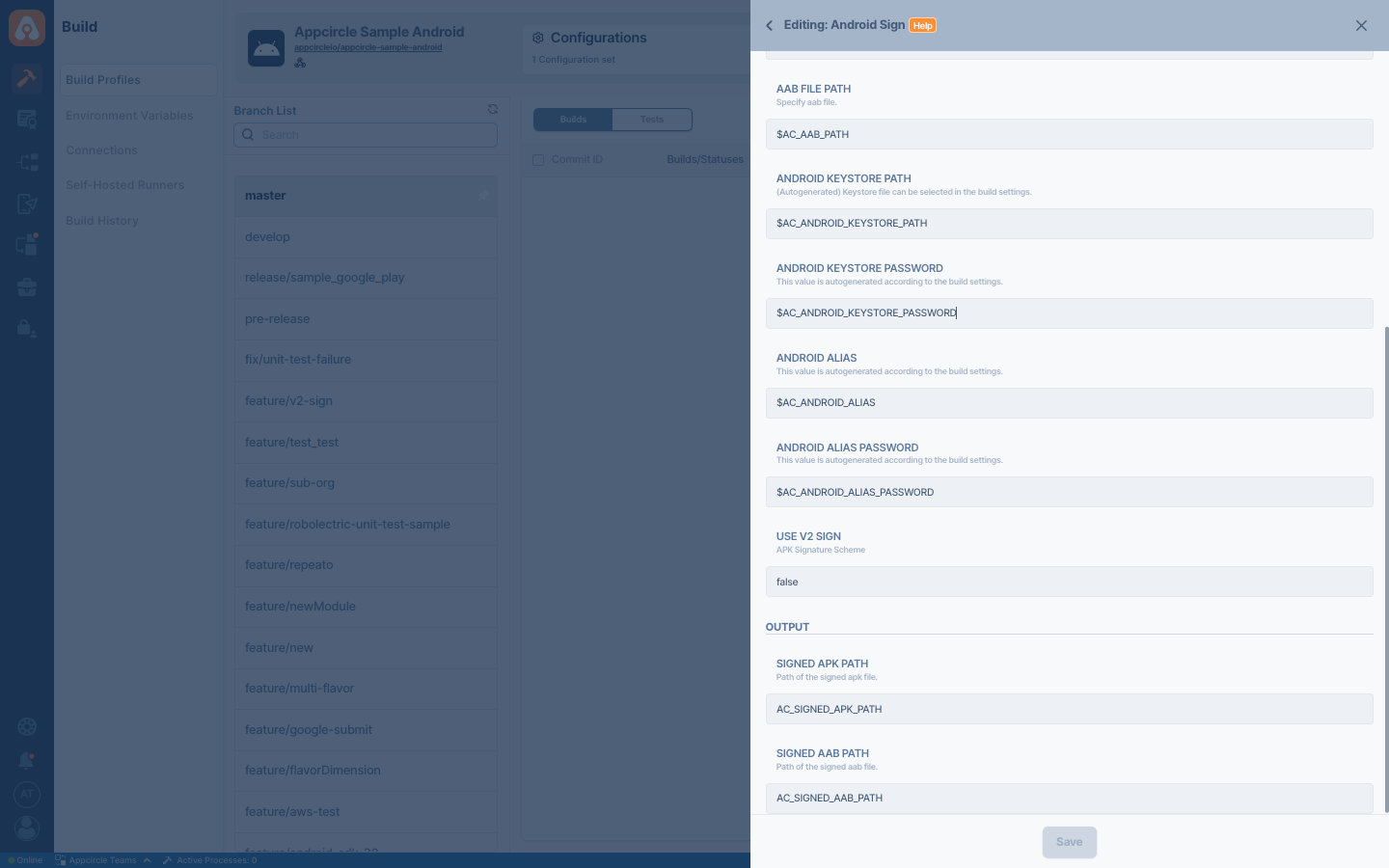
| Variable Name | Description |
|---|---|
AC_SIGNED_APK_PATH | Path for the signed APK file output. If an APK file is provided as input, the signed app will also be in APK format. |
AC_SIGNED_AAB_PATH | Path for the signed App Bundle file output. If an AAB file is provided as input, the signed app will also be in AAB format. |
If both input value types (AAB and APK) are provided, the same type of signed app will be generated for both.
To access the source code of this component, please use the following link:
FAQ
The Android Sign step is often where most Android-related issues arise. The most frequently asked questions are listed below:
“Package invalid” Error After Installing an APK
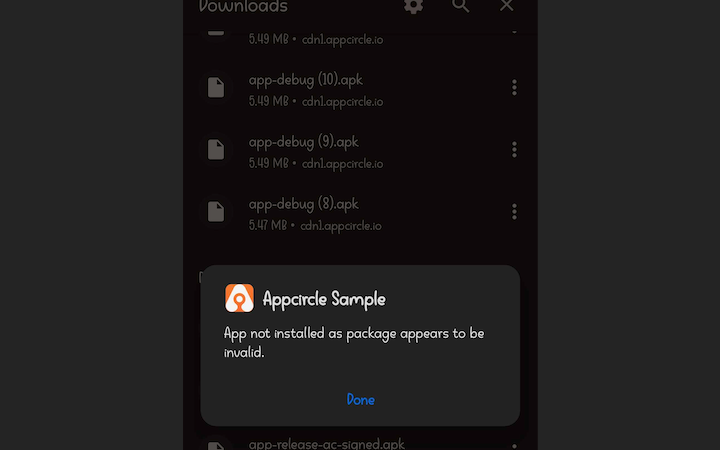
Users may encounter a “App not installed as package appears to be invalid.” error when attempting to launch an application after successfully installing an APK on an Android device. Although the installation appears to complete without errors, the app fails to open.
This issue is typically related to APK integrity, signing configuration, or device compatibility.
Possible causes and solutions:
1. APK Is Signed Incorrectly or Not Signed
Cause:
Android requires all APKs to be properly signed. An incorrect signing configuration or a missing signature can result in a “Package invalid” error at runtime.
How to Check:
- Use
apksigner verifyorjarsigner -verifyto confirm the APK is signed. - Verify that the correct keystore, key alias, and passwords are used in Appcircle.
Solution:
- Ensure the Android Sign step is configured correctly in your Appcircle workflow.
- Confirm that the signing key matches the one used for previous releases of the app.
2. APK Is Corrupted or Incomplete
Cause:
The APK file may be partially uploaded, corrupted during download, or incorrectly generated during the build process.
How to Check:
- Try installing the APK on another device or emulator.
- Verify the APK file size and compare it with previous successful builds.
Solution:
- Rebuild the APK from Appcircle.
- Re-download the APK and ensure the transfer process completes successfully.
3. Package Name Mismatch
Cause:
The APK’s applicationId (package name) does not match the already installed app on the device, or conflicts with an existing package signed with a different key.
How to Check:
- Inspect the
applicationIdin your Gradle configuration. - Check whether another version of the app with the same package name is already installed on the device.
Solution:
- Uninstall any existing version of the app before installing the new APK.
- Ensure consistency between the package name and the signing key across builds.
4. Unsupported Architecture or Android Version
Cause: The APK targets an ABI (CPU architecture) or Android SDK version that is not supported by the device.
How to Check:
- Verify the device’s Android version and CPU architecture (ARM, ARM64, x86).
- Inspect the APK’s
minSdkVersion,targetSdkVersion, and supported ABIs.
Solution:
- Build a universal APK or ensure the correct ABI splits are included.
- Adjust
minSdkVersionif the device runs an older Android version.
Summary
A “Package invalid” error is most commonly related to signing issues, corrupted APK files, package name conflicts, or device incompatibility. Carefully validating the signing configuration and build outputs in Appcircle usually resolves the issue quickly.
If the problem persists after verifying the points above, rebuilding the application with a clean workflow and rechecking the Android Sign step is strongly recommended.