Xcodebuild for Devices (Archive & Export)
This step builds your application for iOS devices in ARM architecture, which is required for the Sharing With Testers feature or any other means of iOS distribution.
This step is the archive and export step. When the step is completed, the .ipa file of the application is generated.
Prerequisites
Before running the Xcodebuild for Devices step, you must complete certain prerequisites, as detailed in the table below:
| Require Workflow Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Git Clone | The repository that needs to be built must be fetched from the Git provider. Xcodebuild for Devices should be used after this step. |
| Xcode Select | In this step, select the Xcode version to build. Xcodebuild for Devices should be used after this step. |
| Cocoapods Install | This step installs all pod dependencies for project. Xcodebuild for Devices should be used after this step. If you use SPM (Swift Package Manager), it is not necessary to use. |
This step should always follow steps that may affect Archive and Export, such as Xcode Select and Cocoapods Install.
Input Variables
This step contains some input variable(s). It needs these variable(s) to work. The table below gives explanation for this variable(s).
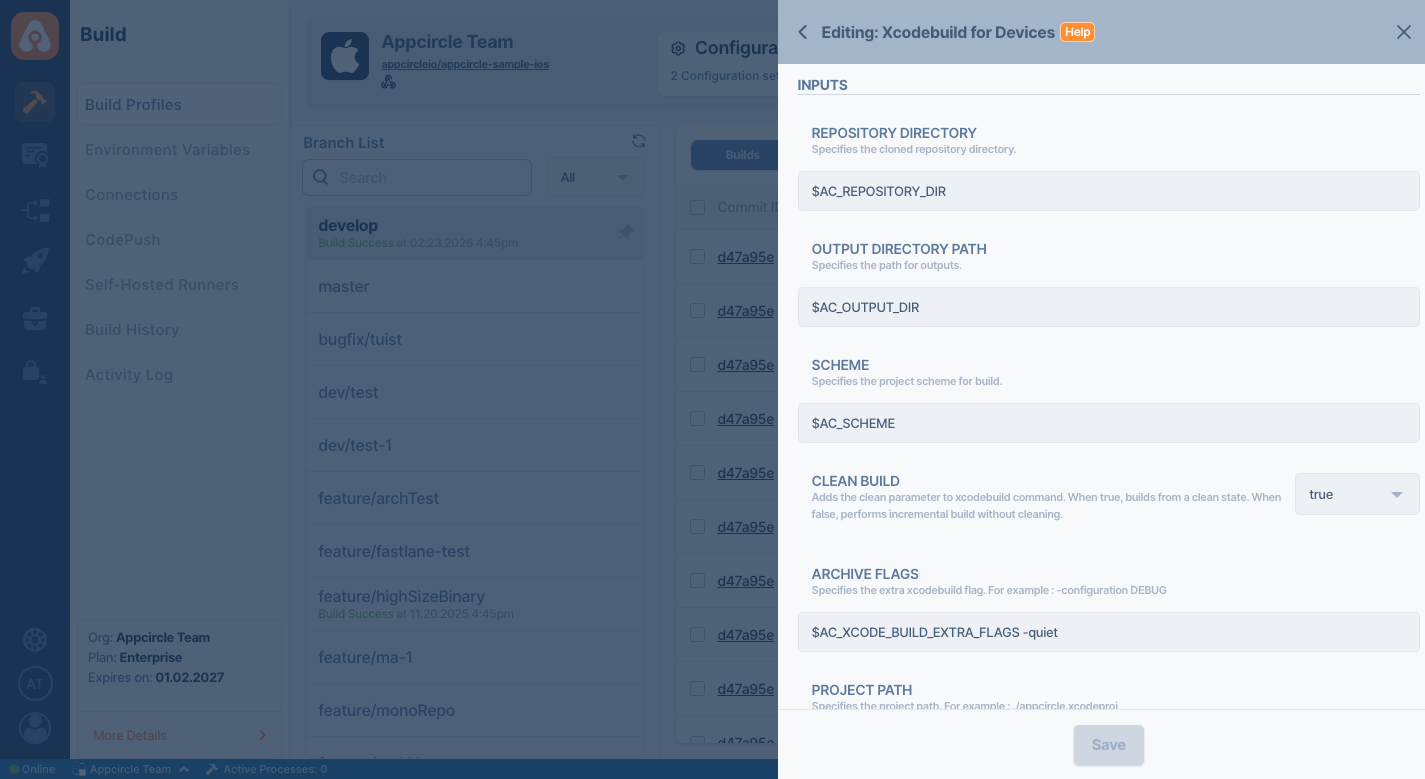
| Variable Name | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
$AC_REPOSITORY_DIR | Specifies the cloned repository directory. This path will be generated after the Git Clone step. | Required |
$AC_OUTPUT_DIR_PATH | This variable specifies the path of the artifacts that will be generated after the build is complete. | Required |
$AC_SCHEME | Specifies the project scheme for build. If you filled in Configuration => Build Scheme, this variable comes from Configuration. | Required |
$AC_CLEAN_BUILD | Adds the clean parameter to xcodebuild command. When false, performs incremental build without cleaning. Default value is true. | Optional |
$AC_ARCHIVE_FLAGS | Specifies the extra xcodebuild flag. For example: -quiet. | Optional |
$AC_PROJECT_PATH | Specifies the project path. For example: ./appcircle.xcodeproj. If you filled in Configuration => Project or Workspace, this variable comes from Configuration. | Required |
$AC_CERTIFICATES | This variable specifies the path of the certificates to be signed. | Required |
$AC_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIERS | This variable holds the Bundle Identifier of the application to be built. | Required |
$AC_PROVISIONING_PROFILES | This variable specifies the path of provisioning profiles to be signed. | Required |
$AC_CONFIGURATION_NAME | You can build your project with any configuration you want. Specify the configuration as hard coded. Appcircle will add automatically this configuration to the xcodebuild command. For example; Debug. | Optional |
$AC_COMPILER_INDEX_STORE_ENABLE | You can disable indexing during the build for faster build. Default value is No. | Optional |
$AC_METHOD_FOR_EXPORT | Describes how Xcode should export the archive. Available options are auto-detect, app-store, ad-hoc, enterprise, development. The default is auto-detect. | Optional |
$AC_TEAMID_FOR_EXPORT | The Developer Portal team to be use for this export. Defaults to the team used to build the archive. | Optional |
$AC_COMPILE_BITCODE_FOR_EXPORT | For non-App Store exports, should Xcode re-compile the app from bitcode? Available options YES, NO. | Optional |
$AC_UPLOAD_BITCODE_FOR_EXPORT | For App Store exports, should the package include a bitcode? Available options YES, NO. | Optional |
$AC_UPLOAD_SYMBOLS_FOR_EXPORT | For App Store exports, should the package include symbols? Available options YES, NO. | Optional |
$AC_ICLOUD_CONTAINER_ENVIRONMENT_FOR_EXPORT | For non-App Store exports, if the app is using CloudKit, this configures the "com.apple.developer.icloud-container-environment" entitlement. Available options Development and Production. | Optional |
$AC_DELETE_ARCHIVE | Delete build.xcarchive file after creating ipa file. | Optional |
If SPM dependencies are kept locally in your project and are already installed, the Xcodebuild for Devices step may fail during the build while resolving the dependencies. For this reason, you can use the -skipPackagePluginValidation parameter in the $AC_ARCHIVE_FLAGS input to prevent reloading dependencies that are already installed in the project.
Note: This may be a security risk if they are not from trusted sources.
Output Variables
The output(s) resulting from the operation of this component are as follows:
| Variable Name | Description |
|---|---|
AC_ARCHIVE_PATH | This is the path created after retrieving the archive. |
AC_ARCHIVE_METADATA_PATH | This is the path created after the metadata is generated. |
AC_EXPORT_DIR | This is the path created when exporting. |
To access the source code of this component, please use the following link:
FAQ
Adding Additional Command to Xcodebuild for Devices Step
To address the need to add a new command after completing the xcodebuild command in the Xcodebuild for Devices step, you can follow the following approach:
- Disable Xcodebuild for Devices step in your workflow.
- Add a new "Custom Script" component instead of Xcodebuild for Devices step.
- Go to Appcircle github profile and navigate to the repository.
- Copy all code lines from the
main.rbfile and paste them into the new Custom Script that you just added in your workflow. - Change the name as Custom Xcodebuild for Devices for this custom script.
- Change "Execute With" picker as Ruby.
- In the Ruby code, you can add the required codes to the end of the
xcodebuildcommand.
Before running the script, some variables must be changed, and new variables must be added to the Custom Script.
First, the output_path global variable should be changed like below in global variables.
...
## Other global variables
...
$output_path = env_has_key("AC_OUTPUT_DIR")
After this, you need to add some parameters to your custom script. The parameters below should be added right after global variables.
AC_COMPILER_INDEX_STORE_ENABLE = "NO"
AC_METHOD_FOR_EXPORT = "auto-detect"
AC_DELETE_ARCHIVE = "false"
AC_ARCHIVE_PATH = "AC_ARCHIVE_PATH"
AC_ARCHIVE_METADATA_PATH = "AC_ARCHIVE_METADATA_PATH"
AC_EXPORT_DIR = "AC_EXPORT_DIR"
In the next step for completing custom script settings, the AC_COMPILER_INDEX_STORE_ENABLE parameter should be equaled with the following parameter:
$compiler_index_store_enable = AC_COMPILER_INDEX_STORE_ENABLE
You should find the line with compiler_index_store_enable and replace it with the above statement.
After these variables were set. There is an archive() function in the Ruby code. First, find the function in the code.
## Archive Functions
def archive()
extname = File.extname($project_path)
command = "xcodebuild -scheme \"#{$scheme}\" clean archive -archivePath \"#{$archive_path}\" -derivedDataPath \"#{$temporary_path}/DerivedData\" -destination \"generic/platform=iOS\""
...
## Other code lines of archive() function
...
At the end of this function, before running the run_command_simple() function, you can add these lines to be able to add additional commands.
...
## Other code lines of archive() function
...
command.concat(" ")
command.concat("Write your command that you want to add here")
command.concat(" ")
run_command_simple(command)
end
For Example
When you need to reduce the verbosity of the xcodebuild logs, you can achieve this by appending the | grep -A 5 error: command to the xcodebuild command to decrease the clutter in the log file.
...
## Other code lines of archive() function
...
command.concat(" ")
command.concat(" | grep -A 5 error:")
command.concat(" ")
run_command_simple(command)
end
Now, the run_command_simple() function will execute your customized xcodebuild command.
How can I resolve the Outputting Keys and Certificates signing error?
Since Appcircle does not have direct access to self-hosted environments, the default versions installed on runners may also have user-generated updates. This error is caused by using OpenSSL by default instead of LibreSSL. If OpenSSL is used instead of LibreSSL for any reason in your self-hosted environments, you will get an error like the one below.
`parse_certificate': Error outputting keys and certificates (RuntimeError)
C05EDAE401000000:error:0308010C:digital envelope routines:inner_evp_generic_fetch:unsupported:crypto/evp/evp_fetch.c:355:Global default library context, Algorithm (RC2-40-CBC : 0), Properties ()
Could not find certificate from <stdin>
Error: Error outputting keys and certificates
C05EDAE401000000:error:0308010C:digital envelope routines:inner_evp_generic_fetch:unsupported:crypto/evp/evp_fetch.c:355:Global default library context, Algorithm (RC2-40-CBC : 0), Properties ()
All packages running in Appcircle cloud environments are controlled by the Appcircle development teams on runners and updated when necessary. One of the packages used on runners is LibreSSL. In Appcircle Cloud environments, the LibreSSL 3.3.6 version on macOS Sonoma and the LibreSSL 2.8.3 version on macOS Monterey are used. For more information, please visit our Build Infrastructure documentation.
However, issues may still occur depending on how the environment is used. If you are working in the cloud environment and the Custom Scripts you use can change or update the packages in our environments. If cloud users encounter such signing errors, it is recommended to check the Custom Scripts used. You can use the example bash script below.
export PATH="/usr/bin:$PATH"
Appcircle's macOS environments use LibreSSL by default. If this default value is changed in any way, the global path must be updated with the script above and LibreSSL must be set as default again. Otherwise, the system will try to find and sign OpenSSL first while the system is running, so if there is a depricated method, it may cause an error during signing.
Note: Please note, the example script given above should be run before the Xcodebuild for Devices step. Otherwise you may keep getting errors during signing.
Although LibreSSL and OpenSSL are alternatives to each other, there are differences between them. LibreSSL comes by default with macOS machines and is managed by Apple. For this reason, since Appcircle does not have direct access to self-hosted environments, some user-side work on runners can replace LibreSSL with OpenSSL or update their versions.
The reason for this error is that the encryption algorithm in the new versions of OpenSSL has been changed. In OpenSSL versions 3 and above, the algorithm named RC2 is marked as legacy. When you encounter this error, you need to change the OpenSSL package on the runners receiving the error to LibreSSL.
The RC2 algorithm is just one example. There are other algorithms and ciphers that OpenSSL has deprecated. Users may encounter other errors with certificates containing other algorithms, such as SHA1. This depends on the encryption algorithm of the certificate the user is using.
For more information about legacy algorithms, please visit the OpenSSL documentation.